Pros and Cons of Muni Bonds Right Now

A municipal bond, often called a muni bond, is a bond issued by a local government or a local government agency such as a housing authority. These bonds often fund roads, schools, airports and seaports, and infrastructure-related repairs.
This is a multitrillion dollar market that has been growing as state and local governments seek more and more funds. There are a number of different bonds issued by states, counties, cities, hospitals, local housing authorities and others.
In addition to the variety of issuers, there are a variety of bonds. Munis can be general obligations of the issuer or the repayment of the bond can be secured by specified revenues.
No matter who issued the bond or what type of bond it is, interest income received by holders of municipal bonds is often free of federal income taxes and is often exempted from state and local income taxes in the state of issue.
The tax free nature of the bonds makes them appealing to many investors. For example, the iShares National Muni Bond ETF (NYSE: MUB) offers a yield of 2.3%, which is equivalent to a yield of 2.9% for a taxpayer with a 22% marginal federal income tax rate and no state income tax. A state income tax could make that yield even more valuable.
To find a similar level of income in government bonds, an investor must accept more risk. For example, if interest rates rise by 1%, the value of long term government bonds could fall by more than 15%. The same increase in interest rates is expected to decrease the value of MUB by about 6%.
The price of MUB is not as volatile as stock market ETFs and is lower than the volatility of some bond funds.
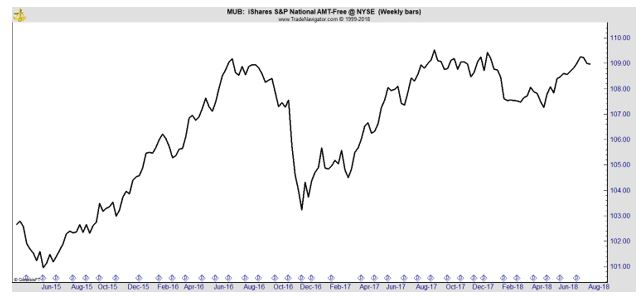
Relative price stability, tax free income and less risk are advantages of investing in municipal bonds. But, there are risks to munis.
More Supply Could Reduce Prices
The laws of supply and demand are well known by investors. When supply exceeds demand, prices fall and when demand exceeds supply, prices rise. In the case of munis, it’s likely supply is set to increase. State and city governments need more money and can’t continue to raise taxes in all areas.
One reason they need more funds is because of unfunded pension liabilities. The chart below shows this problem has been growing in recent years.
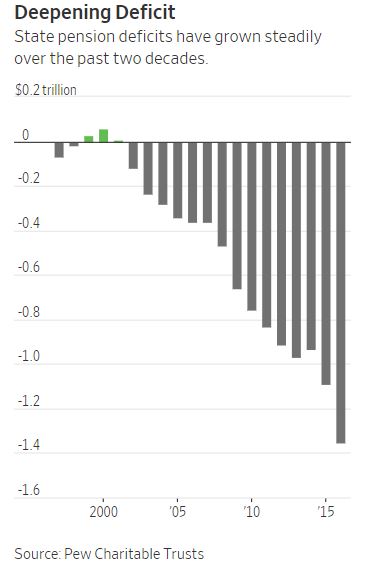
Source: The Wall Street Journal
This trend seems unlikely to be reversed in the next few years. Notice that the amount of the state pension deficits have been rising even as the stock market has been moving up in the past ten years. With the bull market likely to end soon, funds could see their unfunded positions increase.
The problem of unfunded liabilities is even larger when local government pensions are included. According to reports, “By one estimate they are short $5 trillion, an amount that is roughly equal to the output of the world’s third-largest economy.”
In addition to pensions, city and state governments face increased costs of operations. They need to fund education, road repairs, local utility services and other government functions. These costs are rising and straining budgets.
Healthcare costs are also rising. That is a well known problem but it’s impact on state and local governments is largely undefined. Part of the costs are captured in pension liabilities but services provided under Medicaid can strain budgets.
Fortunately, governments do have some room to raise taxes. The dollar amount of state and local tax receipts is below its all time highs but that is largely a function of slow wage growth.
Source: Federal Reserve
In a recession, it could be difficult to raise taxes and receipts are likely to decrease when the demand for services rise.
Risks Include Local Politics
One interesting research report recently identified a risk some investors may not be aware of. The risk is that rates will rise, and prices of the bonds will fall as newspapers close. Several big city newspapers including the New York Daily News have been laying off staff and decreasing local coverage.
According to Barron’s, “When local papers close, it costs the local government money, according to a paper presented at the 2018 Municipal Finance Conference at the Brookings Institution.
“Local newspapers hold their governments accountable,” wrote Pengjie Gao of the University of Notre Dame, and Chang Lee and Dermot Murphy of the University of Illinois at Chicago, in “Financing Dies in Darkness? The Impact of Newspaper Closures on Public Finance.”
They compared municipal-bond yields for counties with three or fewer papers before and after a closure with counties with zero closures, from 1996 through 2015.
“The municipal-bond market provides an ideal setting for our study because the individual bonds are largely bought and sold by local investors, providing a more direct link between local media shocks and securities prices,” they wrote.
They found that three years after a newspaper shuts down, market yields climb by 6.4 basis points, and for newly issued bonds, yields are 5.5 basis points higher.
The effect is even more pronounced in areas with already bad governance: The authors found that newspaper closures increase borrowing costs by 12.3 basis points in states with low-quality governance, compared with only 5.5 basis points in states with high-quality governance.
And for revenue bonds, which are backed by project-specific cash flows, secondary and offering yields climbed 9.9 and 10.6 basis points, respectively. (Bond prices and yields move in opposite directions.)
The authors believe that as local papers decrease coverage of city politics, there’s less information available to the public. That increases the risk of government waste and results in a premium for the bonds.
Overall, the risks of munis are significant but the income they offer could be appealing to investors with significant tax bills. Tax reform could lower bills for many individuals but taxes will still be higher, in dollar terms, than many investors want to pay. That could fuel demand for munis.
And, all things considered, the risks of munis are in many ways similar to the risks of Treasuries and the higher income could be appealing as rates remain low.
You can click here for more market related information.